
Fresco of a lion in Babylon
| Ancients cities beneath the sands |
Ancient Anatobia (now Turkey) yields a great abundance of archaeological material. Here was found the remains of one of the most ancient cities of the past; Catal Hoyuk, in the Konya region. It was discovered by the British archaeologist James Mellart in 1961. It was a strange place inhabited around 6500 BC by people who lived for more than 500 years.The city had no streets and was built expressly as a fortress with very small observation holes in the exterior walls. The tiny houses were built very close together, in fact they were interconnected by ladders that reached from one roof to the next, forming a continuous terrace. When an invader approached the ladders were removed and the people defended themselves from their roof terraces.
On the site of the ancient city have been found pictures representing the "mother goddess" the symbol of protection and fertility as well as a god with an erect phallus in partnership with a bull (like Min and Apis in Egypt). However, no altar or table for sacrifices was found which leads us to believe that the ritual of sacrifice entered into religious practice later. The bodies of the dead were offered to the vultures, then the bones were buried under central flagstones of the town.
Catal Hoyuk and its more famous sister city Jericho are not unique and numerous cities still lie buried beneath the sands ready to reveal to us their ancient secrets.
The period of the great invasions of the Middle East
Even whilst Hammurabi reigned in Babylon, the Hittites of Anatolia were attacking the towns and the villages of Northern Mesopotamia in armed savage bands. This lasted for longer than a century after Hammurabi died.Then the lords regrouped under their ruler king Mursil the 1st (1620 to 1590 BC) and decided to lay siege to the capital of the kingdom of BABYLON. Despite the strong fortifications, the city fell in 1595 BC.
Many men were tortured and put to death, many women and children were led into slavery along with the great treasures of the Hammurabi dynasty.
" Mursil went to Babylon and, like a tiger, sacked Babylon, with the help of the goddess Arinna, then he took the prisoners and all the treasures of Babylon to Hattusha, (including the great golden statue of the god Marduk). "After making incursions as far as Chaldea, the cruel Hittites departed, leaving the land in such a pitiful state that it was easy prey for future invaders.
These were the KASSITES, who also crossed Anatolia, invaded Babylon and established a dynasty which lasted for 4 centuries.
From the other side, Assyria was conquered by the Hurrians, who also traversed Anatolia. Less savage than their predecessors, they reconstructed the sacked temples and adopted the language of the conquered people, but proclaimed their sovereignty over Assyria.
Around 1560BC, the kingdom of the MITANNI emerged. It extended the length of Mount Yaurus, between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Then in 1336BC, the kingdom took over the Assynians, Northern Syria and Eastern Kurdistan. The exact location of their capital Wahshukanni is still uncertain.
In Egypt, the Pharaoh ASMOSIS 1st of the 8th dynasty (1576-1546BC), chased the HYKSOS from the Nile Delta, then Thoutmosis III (1504-1450BC) after several military campaigns, annexed Syria and Canaan . A peace treaty between Egypt and the MITANNI was sealed by the marriage of Amenophis III (1417-1379BC) to Gilu Hepa (the daughter of Shuttarna II, the king of the Mitanni, who by this treaty kept Syria and left Canaan to the Egyptians).
In 1380BC, Suppiluliuma succeeded to the Hittite throne. He was young ,ambitious and held back the barbarian Gascas extending his kingdom as far as Lebanon and Northern Syria.
During 1304 to 1237 BC, Ramses II held power in Egypt. Outside Kadesh, there was a terrible clash between the Hittites and the Egyptians in 1300BC, where both camps claimed a victory despite heavy loss of life on both sides. Peace was signed and Ramses II offered the hand of one of his daughters to the future king Hattousil III to seal the Alliance.
In Mesopotamia, in 1347 BC began a series of wars for possession of the territories. After these struggles, Assynia and Babylon were liberated from Egypt.
In 1335 BC, there was a period of Bablo-Assyrian conflict which led to declaration of war from Elam (Northern Persia) against Babylon, which was thus attached on two fronts.
The Period of Assyrian Power
During the period 1274 to 1245BC Salmanasar lst ruled in Assyria. He was a great warrior who was unafraid of the lords who attached the borders of his country. He crossed the Urartu mounting in Armenia to give battle to the ferocious Gouttis.In 1235BC, Tukulti-Ninurta, the son of Salmanasar, won a great victory over the Babylonian king Kashtiliah (whom he presented to his god Ashur, bound up like a lamb ready for slaughtering). Babylon was annexed until 1218BC and kept under Assyrian protection.
In 1200BC, the Mouskis, (barbaric Armenians) who were allied to the (Gasgas and the Phrygians), destroyed the Hittite empire, burning the capital Hattussha, as well as numerous cities in the northern part of Assyria .
In 1160BC, Shutruk Nahhunte invaded Mesopotamia, plundering all its wealth. Even the famous tablets of the Hammurabi code were transported to Susa.
In 1157BC, Babylon succumbed to Elamite attacks and the great golden status of the god Marduk was again removed.
This was almost the end of the Kassite empire and Babylon was not taken by the Elamites again until 1130BC, by Nimurta Nadin Shumi.
In Palestine, a new nation, "the Hebrews", former slaves of the Egyptians, had conquered Canaan 2 centuries before. At this time they had no king but were administered by judges.
The Medes crossed the Caucasus into Iran, followed by the Persians, who went via Zagnos to settle in the region that is now Shiraz. The Parths and the Hairawas settled Turkestan and Afghanistan.
In Babylon, the third king of the new dynasty of Isin (succeeding his father Ninurta Nadin-shumi) was NEBUCHADNESOR 1st who ruled from 1124 to 1103BC. Continuing his father's work, he confronted the Elamites but was defeated in the first battle. He won the second battle thanks to the help of an Elamite chief who changed sides : Shitti-Marduk, to whom Nebuchadnesor promised land and states. Nebuchadnesor pillaged Susa and took the great statue of Marduk back to Babylon. Several kings succeeded him in Assyria and Babylon without distinguishing themselves.

Fresco of a lion in Babylon
ASSURNARZIPAL II : a cruel and bloodthirsty king
In 883BC, a cruel and bloodthirsty king named ASSURNARZIPAL II came to the throne. He never laughed and liked to watch his prisoners tortured. He had the rebel chiefs skinned alive and their skins displayed on pillars. He had them impaled on stakes or hung their heads on trees about the city. His sadistic nature enjoyed torturing and burning alive women and children by thousands or drowning them in the Euphrates...As he did not feel secure in ASSUR he built a new capital at Kahlu (or Kalku) where he constructed a palace and fortress protected by the rivers Tigris and Zab. The work was done by miserable slaves and lasted 10 years. The fear he inspired paralyzed his neighbors, especially when he went to help himself to material from Syria and cedars from Lebanon. The Arameans and Neo-Hittites feared him so much that they showered him with presents !
Why do we associate the palace at Kahlu with that of the legendary Nemrod ? Was there some kind of connection between Assurnazipal II and the famous mystical character Nemrod, who appeared in history as a king greedy for tributes with effeminate manners and perverse morals? Why does Jewish mythology name Nemrod as the instigator of a huge building which was compared to the tower of Babel, which was also built by masses of foreign slaves speaking unknown tongues and like the palace of Assurnarzipal II was the scene of orgies and debauchery. When the Babel tower had been almost destroyed, it had been rebuilt by slaves, notably the Jews who had been exiled by Nebuchadnesor II ?
This may explain the aggressiveness of his son SALMANASAR III, who succeeded him and spent almost his whole reign fighting the neighboring countries: Syria, Israel (where king ACHAB of Samara, husband of the terrible Jezebel of Tyre, allied himself with his former enemies of Damas against SALAMANSAR III), the Persian Gulf, Armenia and several other provinces...
In 850BC, Marduk-zakir shumi, king of Babylon appealed for aid from SALMANAZAR to aid his country of the Arameans, who wanted to put his brother on the throne. Salamanazar chased out the Aramens but vassalized Babylon.
In 841BC, the Assyrian king organized a campaign against the usupper Hazael of Damas who had assassinated the Syrian ex-king. Hazael lost the battle and locked himself in behind the rampant SALAMANZAR III attacked the coast of Lebanon and demanded tributes from the towns of Tyre and Sidon and also from JEHU, king of Israel (841 to 814BC) who wanted to get rid of the avaricious Assyrian.
In 827BC, there was a great revolt in Assyria; 26 towns, including Assur and Ninevah rebelled making the king's son their leader. The people demanded fewer taxes and a greater share in the wealth of the country. The sickly old king gave up the throne to his son Shami Adad V and died 3 years later.
SHAMI-ADAD (824-810BC) fought the rebels for 5 years. He made Ninevah the new capital of Assyria. Leading 3 campaigns against the Babylonians, he entered Babylon and proclaimed himself king of Sumer and Akkad. As his heir was very young when he died in 811BC, his favorite wife Sammuramat became regent. She was from a foreign country and greatly missed the green verdure of her native land. For this reason, her husband built her the glorious Hanging Gardens of Babylon, which were considered to be one of the 7 wonders of the ancient world. Sammuramat herself entered into legend and later became identified with the legendary queen Seminaris.

Protective winged Genius - Palace at Khorsabad - 8th Century
BC
Around 800BC, Babylon fell into a state of anarchy and for several years no king was elected !From 746BC to 724BC, TEGLATH PHALAZAR III ruled in Assyria an ambitious and pugnacious man. He assembled an army of Assyrians and foreign mercenaries. He organized the massive deportation of colonists - Celaldeans, Syrians and Glamites mainly poor peasants who were obliged to travel on foot or pull chariots for thousands of kilometers to get to the country designated by royal decree. Thus in 15 years, TEGLATH PHALAZAR had transferred 215,000 Babylonian colonists to Assyria and move than 30,000 Syrians into the mountains of Zagros, which themselves were replaced by 25,000 Arameans installed beside the Tigris !
As protector of Babylon, Teglath-Phalazar had to intervene in Lower Mesopotamia at the request of Nabonassar, king of Babylon. He conquered and vasoalized NW Syria, and Phoenicia. Terrified, the princes of Cilicia, Menahem the king of Israel, Razin king of Damas and 2 couriers Arabian queens: Zabibe and Samsi sent ambassadors leaving gold and gifts to the great Teglath Phalazar !
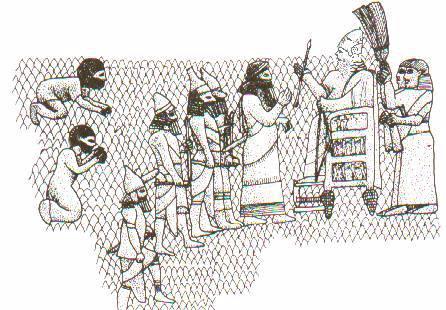
Assyrian Sovereign receiving the submission of the vanquished -
British Museum
The fall and exile
of the kingdom of Israel
and the overthrow of its capital:
SAMARIA
In 726BC, his son SALMANAZAR V started a 5 year reign over Assyria. He annexed Cilicia and took Samaria just before his death, inflecting a terrible 3 year siege on the Samaritans but he was gradually replaced by his brother SARGON II, who killed him and took his crown.If we remember in 931BC king Solomon's great kingdom was divided into 2 between his two sons :
1. ROBOAM, who was the first king of Israel, installing his capital at Samaria. Twenty kings succeeded him until the fall of Samaria and of his son Hosea in 712BC (the last king of Israel).
2. JEROBOAM, who inherited the throne of Jerusalem, giving the name of JUDAH to his new kingdom.
Thus it was in 721BC that the Samaritans surrendered to the Assyrians king Salmanazar V, who transported them to Assyria to the banks of the Chabor (Zaba Ellu, a tributary of the Tigris to the place near Ninevah where such great work of construction was soon to start.
Galilee and Samaria thus became sparsely inhabited so some Arab families settled on the abandoned land, as well as many CHU colonists (from the banks of the Persian river Schuth.) They came under the rule of the Assyrian dictatorship.
As the foreign women were often very beautiful, many mixed marriages took place between the Jews who had escaped deportation and the colonists (who were often very poor) and had been forced to live as exiles. Samaria, had been taken and sacked but Jerusalem and its king Achaz had to submit to Teglath-Phalazar. He not only paid him tribute but had to accept the authority of the Assyrian clergy, who made the Hebrews build many altars and sacrifices to the gods of the Assyrians.
The reign of SARGON II in ASSYRIA
From 722BC to 705 Sargon II usurped the power of his brother and conquered and deported the Samaritans. The latter (along with many slaves from other countries) built for Sargon a huge citadel surrounded by high walls and towers to protect his new palace built beside a large ziqqurat with 7 floors, filled with temples to pagan gods (just like the famous Tower of Babel.) Also, in the center of this fortified village were luxurious living quarters for the dignitaries of the kingdom.
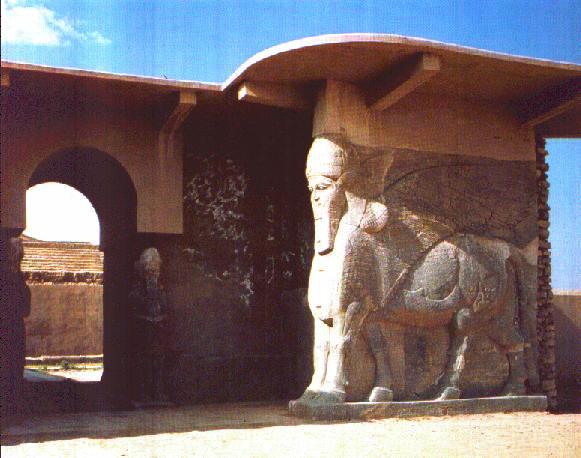

The bulls gate of the palace of Sargon in Dur-Sharrukin
(Khorsabad)
Like Assurnazipal II before him, Sargon II built this imposing citadel (named Dur-Sharrukin and near to the present village of Khorsabat) 25 km from Ninevah. Sargon insisted that his huge palace be surrounded by a terrace 15 meters high so that his view would not be spoiled by the shadow of the ramparts.During the construction (which lasted 16 years) thousands of slaves died of dehydration in the implacable Iranian sun. Also this great citadel was hardly used because after Sargon's death, his successors preferred their former capital at Ninevah, where life was pleasanter.
Sargon only used his palace for a few months, as he died within a year of his official inauguration.
As the inheritance was fiercely contested, the new king took the name SARGON which means "the legitimate king" but this did not prevent revolt throughout the land and even the former capital Assur was among the contestants.
After taking power, Sargon had to put down several revolts and to compensate for the repression he promised to reduce taxes, which had been started by his predecessor Salmanazar V. Suddenly the kingdom of Babylon refused to give him allegiance and pay a tribute, and Merodach-Baladan crowned himself king of Babylon and made an alliance with the king of Elam.
War was inevitable and the conflict between the 3 armies took place near Der in 720BC. Even though Sargon declared himself victor, in reality there was neither victor nor vanquished since Merodach-Baladan II continued to reign in Babylon until 710BC. Babylon would pay for its rebellion.
Still in 720BC, the revolt, the Syrian king Hama ILU-BI'DI made an alliance with 3 other Syrian governors, of Damascus, Arpad and the king HANUNA of Gaza. The pharaoh also sent an army and a general to help the rebels, but Sargon overpowered them all at Qarqar. Anticipating his defeat, the Egyptian general disappeared, whilst his men were slaughtered. As for Hanuna, he survived the battle, but was skined alive...
The fighting did not end there : there was victory against the rebel king IMANI, and the annexation of his country. In 714BC, Sargon decided to ascend the mountains of Zagros, then took all his cavalry, his infantry and chariots towards Lake Urmia and Lake Van. Then he attacked the Urartu capital, MUSASIR, penetrating the centre of the city, which had been thought to be impenetrable!
Knowing the ways of Sargon, the king of Ourartou, named URZANA, decided to take his own life rather than being burnt to death. Ourartou, demoralized, was annexed into the empire, and never regained its greatness.
In 717BC, Sargon invaded the independent kingdom of Karkamish in Syria, and conquered in 5 years all the neo-Hittites of the Taurus, such as Cilicia, Gurgum, Milid and part of Tabal.
Sargon added 2 new states to his empire in 709BC, Cyprus and Phoenicia, both of which had to pay him large tributes.
Sargon II died in 705BC whilst campaigning in Tabal, near the Taurus. His son Sennacherib and his successors abandonned the new citadel at Dur-Sharrukin, preferring to return to Ninevah.
SENNACHERIB AND king EZECHIAS
SENNACHERIB succeeded Sargon and reigned from 705 to 681BC. He inherited an empire, but also many problems which had been caused by his predecessors' continual battles against Elam.
In Jerusalem the situation was not much better. King ACHAZ (736 to 716BC) courted disaster by starting a cult to idols in the temple of Yahweh, and promoted his own paganism and submisssion to the Assyrians by sacrificing young children to these idols in the Valley of Hinom, (where the Canaanites had previously sacrificed infants to the cruel god Moloch). Jerusalem was beseiged by Israel and by king Aram, so Achaz called for help from king Teglath Phalasar III of Assyria, whose vassal he had become.
In 714BC, 6 years after the fall of Hosea at Samaria, Ezechias succeeded his father Achaz to the throne. During this time, the great prophet Isaiah lived in Jerusalem; as advisor to king Ezechias he managed to restore the religion of Yahweh, and destroy all the idols in the temple.
In 701BC Egyptian propaganda inspired the kings of Sidon, Ascalon and Jerusalem to revolt against the Assyrians. Immediately, Sennacherib launched a campaign to put down the revolt of Sidon and Ascalon. Only Jerusalem remained, a fortified city high on a mountain, and he beseiged it.
During the seige, Ezechias gave the order to dig a subterranean channel through Mount Zion, to allow water from Gilhon to flow to the sacred city. It is rather difficult to understand the reasoning behind the enormous tribute imposed by the Assyrian king on Ezechias, on condition that the seige be ended.
The second book of Kings (chap.18), verse 15 says "the Jews paid 30 talents OR 800 siver talents".
- then he gave all the treasure to the temple, adding the royal treasure amassed by his predecessors--even taking the gold from the lintels and the columns of Solomon's temple!...
But the seige was not lifted just for that! Although Jerusalem had been sacked of all its wealth, this did not greatly interest the Assyrian king.
Let us not forget that Ezechias was Jewish! We must move on to the the episode of the angel who killed 185,000 people in a plague during another campaign against Elam (according to the historian Herodotus), who traveled through the Middle East around 450BC to "see the locations of history which had been mentioned in his 9 books".
We also know that Ezechias had blocked off all the water sources around Jerusalem and that Sennacherib's army was desperately short of water. This technique was often used to kill their attackers from the west. Thus Sennacherib was paid for his exploits, and he returned to Ninevah !
At the same time, (according to the book of Kings(ch20 v12), Merodac Baladan III, king of Babylon, an ally of Elam, sent his ambassador with a gift for Ezechias to reassure him about rumours which were heard about his losses. Ezechias showed him the place where all his treasures were hidden : gold, siver and all his personal wealth!
Isaiah was very angry and predicted to Ezechias that the next removal of all his riches would be to ... Babylon !
The Destruction of BABYLON by SENNACHERIB in 689 BC
Merodach Baladan II had left Babylon in 710 BC to take refuge with his family in Elam. Was it him or his son who returned in 703 BC with Elamite troops to reconquer the throne of Babylon? He had only just taken the throne when his subjects rebelled against the Assyrian yoke. Sennacherib who had retuned two years before from his campaign in Jerusalem, lost no time in mobilizing his army in readiness to retake Babylon.Sennacherib won the battle of Kish, and destroyed the Elamite troops as they were retreating. Then he followed Merodach Baladan, who was obliged to take refuge in the marshes in the south of the country.
Sennacherib could from now on quietly plunder the royal palace of his rival and installed there in his place as governor a young Babylonian named Bel-Ibni, who had been raised in the Assyrian palace.
As punishment for their revolt 200,000 Babylonians and Arameans were deported to the north of Assyria, to be able " to supervise them better ".
Three years passed and there was a new uprising of Merodach-Baladan, so Sennacherib returned to restore calm, and execute the rebels. Then he relieved Bêl-Ibni and replaced him by his son, Ashur-nadin-shumi. Then in 690 BC, suddenly Sennacherib decided to leave to launch a campaign on the other side of the Persian gulf : with the hope of plundering several rich coastal cities of Elam.
At once HALLUSHU king of Elam seized the oportunity of invading Babylon and seized Sippar, then made his entry into Babylon, (where they returned to him the son of Sennacherib, who had never returned from his captivity in Elam).
The answer was not long in coming, as this same year there took place a great confrontation between Assyria and Elam (the future Persia), against HALULE on the Tigris . Even though the Elamites returned home without much glory, they inflicted great damage on the Assyrian army !
To be avenged, Sennacherib decided in 689 BC to attack BABYLON by surprise...
- (Sennacherib) I saved neither the young people, nor the old men, I filled the streets with their corpses. I devastated all the city and consumed it in flames, so that in the future even the site of the temples will be forgotten...
Actually, the tower of Babel was not destroyed and the soldiers were more occupied with plundering, rape and murder than destroying the houses. Fire caused great devastation in the temples and public buildings.
To calm his anger, Sennacherib left with his troops and advanced towards the Isthmus of Suez. Herodotus tells that during the night an immense invasion of famished rats invaded the Assyrian camp. They ate all the leather and the fabric of the tents, then because they carried contaminated fleas, they infected thousands of men with the plague...
The justice of the sky had come down upon them, and Sennacherib, who saw it as a punishment of the gods, returned immediately to Ninevah. Seven years later, in the first days 681 BC, he was stabbed by one his sons while he prayed to the god Nabu (the Babylonian god of letters and science) in his temple.
Other "lessons of Providence" in the History :
1. The English king : RICHARD LION HEART
Following the great battle of Hattin, Jerusalem was taken on October 2 1187 by the Emir Saladin, who let go the civilians, but kept captive 2700 Franks brought back from the plateau of Hattin. Immediately Gregory VII declared the third crusade:Already the emperor Barberouss arrives to Turkey with 250 000 crusaders! With so many men he could have changed the entire history of the crusades, but Barberouss instead was drowned in a small river of the Taurus! His army disintegregated and the majority of the soldiers returned home.
Next, Philippe-Auguste and RICHARD LION HEART beseiged Saint Joan of Arc in Palestine. The seige of Arc started in August 1191 and lasted two years! Wearied, the majority of the leaders of the crusaders, except Richard, returned to their country.
In July 1191, the people besieged with Saint Joan of Arc gave themselves up on the promise of an enormous ransom fixed at 200 000 dinars-GOLD. But at the end of fifteen days, Richard became impatient and gave the command to decapitate the 2700 men and to pass through the 300 Moslem women of Acre with a sword...Saladin, who still had in Jerusalem the 2700 prisoners had promised to execute them, but his religion and nobility of soul prohibited him from perpetrating such a crime !
Richard would never take Jerusalem! On October 9 he left Palestine and on the return journey, duke Leopold's men, whom he had insulted before the ramparts of Acre captured him and sold him to the German Emperor Henry VI who released him for an enormous ransom after TWO YEARS of detention...
2. The conquest of the NEW WORLD
Ferdinand and Isabella ordered that all the gold of the New World be brought back to Spain. On July 3, 1502BC thirty ships from Bobadilla were travelling to Spain with the equivalent of 200 000 ducas on board in statuettes of gold, representing the effigies of the gods of the Indians of the islands and Americas.Suddenly a terrible storm arose and wrecked the whole of the fleet... Only one caravel would survive the shipwreck to announce to the king that the lingots were now on the ocean floor. The Indian gods had not appreciated the sacrilege of the Spaniards.
3. CHARLES QUINT before Algiers
The great Spanish emperor, and defender of the Catholic faith would fight during his entire reign against the Protestants, the Moslems, the Jews and the savages of the New World, who were to die in tens of millions in forty years.In 1527, Charles lets his imperial troops sack Rome. In 1535, he was present at the capture of Tunis, where in front of his eyes, his troops massacred the Moslems, raped the women and plundered the city, which swam in a blood bath. A little later, he wanted to repeat this kind of massacre on Algiers, and prepared to attack with his fleet of 180 ships fully armed, when suddenly a formidable storm broke out and carries to the bottom of the sea most of his warships containing most of his army... !
4. NAPOLEON at Jaffa and St Joan of Arc
On June 22, 1798 Bonaparte had just arrived in Egypt, and thus addressed his men : " Soldiers !
- You are about to undertake a conquest whose effects on civilization are incalculable. We will succeed because destiny is on our side... (!)
- The people with whom we will live are Moslems, but do not contradict them, have respect for their Muftis and their beliefs as you have for the rabbis and bishops.
- The Roman legions protected all religions, they said that all men are equal in front of God !
- Only differences : are wisdom, their talents and virtues.
- What destroyed, if it was not avarice, injustice and tyranny, the Mameluke people, who oppressed the poor ? Moreover didn't we destroy the pope who said that it was necessary to make war on the Moslems ? "
Having conquered Egypt, Napoleon dreamed of conquering the Turkish empire,but it was first necessary to conquer Syria, Jaffa, and Saint-Joan of Arc to open the road to Istanbul...
February 10, 1799 Bonaparte departed for Syria and in less than one month the south coast of Palestine was conquered.
Jaffa was taken by storm by four divisions, who cut the throats of the Moslem soldiers, forced open the gates of the harems, raped the women and seized all the treasure.
As nobody obeyed the commands any more, General Robin, charged his own soldiers to stop the madness of the violence.
There remained about three thousand men that the soldiers had wanted to burn alive! But Beauharnais and Crozier refused, thinking that Bonaparte wanted to negotiate with the garrison. The besieged answered that they would give up if they had a promise of safety, and if not, they would fight until death. The two aides-de-camp took up this promise and brought the prisoners before Bonaparte who exclaimed :
- But what can I do with these prisoners? I can only let them die. I can release only the women and children, but not the armed men!
Pretending to be unaware of the promise, Bonaparte made the decision to exterminate them in spite of the courageous intervention of Berthier, who left, his head bowed. Then the butchery started.
Many children who had clung to their fathers were found among the victims... And the massacres continued from the 8th to March 10, 1799...
But the Englishman John Christopher Herold wrote that on March 8, God sent the plague to devastate the French Army... Many soldiers, covered with bubos died in a few days and soon half of the garrison succumbed to the epidemic, only one man in twelve escaped from it...
Bonaparte had believed that the Turks of St Joan of Arc would be horrified by the example at Jaffa, and were going to surrender immediately, but the opposite occurred. The men wanted to fight until the last! Bonaparte who had dreamed of conquering all of the East returned to Paris without having been able to take what he called: the shack of Arc...
Even if all the interventions of destiny are not so obvious, there are in the History of the World a great number of examples of what we call Providence, which changes, sometimes in very surprising ways, the destiny of men with egoistical ambitions.
The Assyrians and Chaldeans believed that "each man is the son of HIS god". This god is his intercessor on his behalf with other more powerful gods, and this is why since the time of UR NAMMU (2112 to 2095 BC), they prayed and spoke to their god while standing before him. Their patron-god held their hand when meeting the great god Enlil, who one day would judge their actions.
This protective god, whom the Babylonians thought of later as good spirits able to protect them from bad demons. Thus the ordinary people, and even the slaves, had hope of a better life in another world .
The history of Jonas in the Bible is an excellent example of the Assyrians fearing the anger of foreign gods, and that antipathy existed already between Arabs and Jews. Like Elias, Jonas (783 to 743 BC) was a prophet of the kingdom of Israel, born close to Nazareth at Gat Hepher, around the time of the taking of Damascus (732 BC) and Samaria (722 BC). Even if certain religious scholars challenge today the validity of his message, the attitude of Jonas was completely in conformity with the spirit of his time.
But Yahweh was not only the God of the Jews, He was, from the dawn of time, the God of all men of goodwill, who would be judged with mercy, taking into account their weaknesses, their ignorance and above all their regard for their fellow men, even though their spirit may have worshiped graven images.
Reign of ASSARHADDON at NINEVAH from 681 to 661 BC
The assassination of Sennacherib opened a serious crisis of succession in Assyria, as the late king had indicated as successor his youngest son Assarhaddon, born to his second wife Zakutu, which explains his assassination by one of the legitimate heirs.His first decree was to order the rebuilding of Babylon, which his father had tried to destroy. The city was enlarged and became even more beautiful than before its destruction.
In 676 BC Phoenicia revolted, Assarhadon was captured and king Abdi-Milkuti of Sidon decapitated, the city was sacked and the inhabitants deported into the heart of Assyria.
Colonists were sent into the new Assyrian province. The provinces of the south remained calm and it was the Babylonians themselves who in 675 BC repulsed the king of Elam : Humban-Haltash, when he tried to invade the country.
In 679 BC Assarhaddon held back an invasion of Scythians and Cimmerians who tried to seize Cilicia, an Assyrian province. The "riders of the Black Sea" then turned against the kingdom of Phrygia, where they seized power in 675 BC. According to Herodotus, Assarhaddon made peace with them by giving one of the his daughters in marriage to the Scythian king Bartatua.
But the main objective of Assarhaddon was to conquer Egypt, which in that time was divided into two large kingdoms, of which that of the Delta was governed by last Libyan king OSORKON II that a prince of Sais : TAHARQA, had dethroned.
The second kingdom of Upper Egypt was controlled by Chabaka, king of Nubia, (Ethiopia), that the new Pharaoh Taharqa had tried in vain to dethrone.
In 679BC Assarhaddon carried out a raid against the frontier town of Arza, but his troops lost the battle against those of Taharqua. (They had come to repress the revolt of the city of Ascalon in 673BC)..
In 671 BC Assarhardon at the head of a large army, tried to invade Egypt, and traveled as far down the Nile as Memphis, where he seized the queen, the harem and the royal heir to Taharqa. Then he installed his own best men in all the conquered cities, and deported to Assyria all the Pharaoh's Kushites. Without forgetting to demand as usual a heavy tribute from all the inhabitants of the conquered areas.
In 669BC Taharqua came down from the High plateau of the Nile, where he had taken refuge, and again took Memphis, trying to incite the inhabitants of the Nile Delta against the Assyrian invader. Assarhaddon had set out to quell the revolt, when suddenly he fell sick and died on the road to Harran.
The succession was wide open, (as Assarhaddon had envisaged one year before,) and had already divided his kingdom at NINEVAH between his two heirs:
ASSURBANIPAL King of Assyria with Ninevah Reigned from 669 to 627BC. |
SHAMASH-SHUMA-UKIN King of Babylon Reigned from 668 to 648BC. |
The reign of King ASSURBANIPAL

Statue of Assurbanipal
From the very start of his reign, Assurbanipal sent his army into Egypt to take again the royal city of Memphis with Taharqua. The latter anticipated his defeat, and had again taken refuge in Upper Egypt. Assurbanipal then decided to find him on the high plateaux of the Nile.He engaged many mercenaries and prepared a massive expedition up the Nile, but king Necho of the Nile Delta gave his support to Taharqua. The Assyrian army crushed that of Necho easily, it killed many rebels and took Necho as a captive to Ninevah. But surprise! Assurbanipal wanted to release the king of Sais and gave him gifts to persuade him to be an ally Meanwhile Taharqua died in the high plateaux of the Nile.
In 664 BC, the son of Taharqua, TANUTAMON succeeded him. Full of vigour, he undertook to reconquer the territories lost by his father. He initially attacked Thebes, where they welcomed him with honors, then he decided to conquer all the cities of the Nile Delta. Necho, who tried to resist to him, was killed in battle. It was at this time that the Assyrian army, hidden very close to Memphis, received the order to march on THEBES and prevent the retreat of Tanutamon.
The temples of Thebes were well and truly sacked, even two obelisks weighing 38 tons each were taken! Tanutamon was defeated, and Assyria became master of the two vassal kingdoms of Egypt, which was entrusted to the new Pharaoh : PSAMMETIK 1st - son of Necho.
In 662 BC Assurbanipal intervened personally against Ba'Al, king of Tyre; he took the fortified city and even forgave the repentant king.
Towards 665BC, king URTAKI of Elam was deposed by a revolt by "Tept-Humban" who seize power and decided in 654BC to invade Babylonia, violating the peace treaty with Assarhaddon. He was immediately chased back to his own land.
In 653BC, PSAMMETIK 1st, wh gained from the war freed Elam and Assyria, rebelled in Egypt and with the assistance of many mercenaries managed to drive out the Assyrians, (Assurbanipal being too engaged in defending his kingdom to intervene)..
Victory had finally returned to Assyria. Tept-Humban was decapitated, and his kingdom of Elam divided into two : one share to be allocated to the son of Urtaki, and the other to a prince of the same dynasty.
652BC brought more trouble. Shamash-shuma-ukin, the brother of Assurbanipal, joined with the Elamites of Susa and rebelled in Babylon! Many countries were involved in this revolt, but the plot was discovered in time. A two year old war took place between the two brothers, then finally the king of Babylon, besieged in his palace, committed suicide by putting fire to it!
In 650BC, Assurbanipal entered Babylon as a victor and decided to deal with the traitors who had helped his brother. Initially it was the Nabatean Arabs, from south of the Dead Sea who were overcome, their herds of camels were taken from them, and then Petra was plundered.
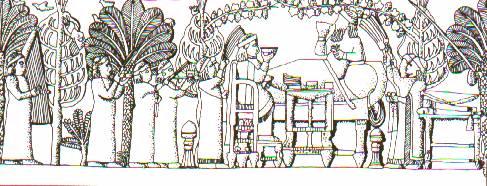
Banquet of Assurbanipal with his wife at the time of the victory
over Elam - British Museum
The Destruction of ELAM
647BC saw the fall of Susa, the capital of ELAM. Its Ziqqurat was razed to the ground, its temples profaned, and the statues of the gods crushed. All Elam was devastated, ransacked, set on fire... The tombs of the former kings were desecrated,and the bones thrown out into the sun so that their souls might never again find rest! And it is here that one can see the hatred and pride of Assurbanipal, who after having driven his brother to suicide, destroyed whole cities and villages, with absolute contempt for any humanitarian principles...Such examples taught a lesson to the neighbouring countries; Cyrus the 1st, king of Persia and Rusa II king of Urartu sent lavish gifts to the all-powerful king of Ninevah, whose palace overflowed with the wealth of Thebes, of Memphis, Tyre, Petra and Susa.
Assurbanipal exulted in all this, while URTAKI was chained and dragged like an animal behind the royal chariot.
o - o - o - o - o - o - o